Hyperautomation: Revolutionizing Business Processes
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, a term that has gained substantial traction in recent years is “Hyperautomation.”
This cutting-edge concept represents a significant shift in the way businesses operate and manage their processes.
Hyperautomation leverages a combination of advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), robotic process automation (RPA),
And more, to automate, streamline, and optimize workflows comprehensively. Hyperautomation also known as Intelligent Automation, Advanced Automation,Automated Workflow.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Intelligent Automation, exploring its definition,
key components, benefits, and real-world applications while adhering to SEO rules and ensuring a high level of readability.
What is Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomation is a term that encompasses a broad spectrum of technological advancements aimed at automating and enhancing various aspects of business processes.
At its core, Intelligent Automation represents the next phase of automation, going beyond mere task automation to create end-to-end automation ecosystems.
It combines multiple technologies to facilitate the automation of both structured and unstructured tasks, resulting in increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Key Components of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is a complex concept with several essential components that work in synergy to deliver its transformative effects. Here are the key components:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML are fundamental to Intelligent Automation. these technologies enable systems to analyze and learn from data, making predictions, and improving processes over time.
Artificial Intelligence they play a crucial role in decision-making and task automation.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
Importantly RPA involves the use of software robots or “bots” to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks.
RPA bots can perform tasks with speed and accuracy, freeing up human employees to focus on more strategic and creative endeavors.
Data Integration and Management:
Another key point Hyperautomation relies on seamless data integration from various sources.
It involves extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) data to ensure that information flows smoothly across systems and processes.
Process Orchestration:
Process orchestration tools enable the automation of end-to-end workflows, coordinating tasks across different systems and departments.
This ensures that processes run smoothly and efficiently. Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is crucial for handling unstructured data, such as text and speech.
It allows systems to understand and interpret human language, making it possible to automate tasks that involve language processing.
Advanced Analytics:
Advanced Automation leverages advanced analytics to gain insights from data and monitor the performance of automated processes continually. Analytics help in identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement
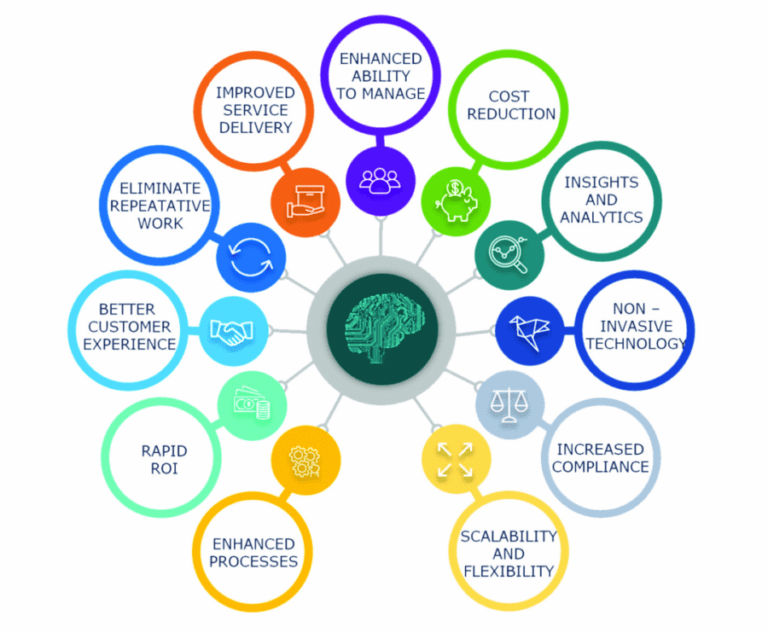
Benefits of Advanced Automation
The adoption of Advanced Automation can bring about a multitude of benefits to organizations across various industries. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
Enhanced Efficiency:
Automated Workflow streamlines workflows, reduces manual intervention, and accelerates task completion. This leads to increased operational efficiency and faster response times.
Cost Reduction:
By automating repetitive tasks and reducing errors, Automated Workflow helps organizations cut operational costs. It also reduces the need for extensive human labor in routine processes.
Improved Accuracy:
Automation minimizes human errors, ensuring that tasks are performed consistently and accurately. This is particularly valuable in critical business processes.
Scalability:
Automated Workflow solutions can be scaled easily to accommodate growing business needs.
As demands increase, organizations can add more automated processes without significant resource investments.
Enhanced Customer Experience:
Automation enables organizations to respond to customer inquiries and requests more quickly, leading to improved customer satisfaction.
Compliance and Risk Management:
Advanced Automation can enforce compliance with regulations and reduce the risk of errors or non-compliance, especially in highly regulated industries.
Employee Productivity:
By automating repetitive tasks, employees can focus on more creative and strategic aspects of their work, enhancing overall productivity and job satisfaction.
Data-Driven Insights:
The data generated by automated processes can provide valuable insights for decision-making and process optimization.
Real-World Applications of Hyperautomation
Hyperautomation is not just a theoretical concept; it has found practical applications across various industries. Let’s explore some real-world use cases:
Finance and Banking:
In the financial sector, Advanced Automation is used to automate routine tasks like data entry, account reconciliation, and fraud detection.
Additionally it also helps in customer onboarding by automating KYC (Know Your Customer) processes, reducing paperwork and processing time.
Manufacturing:
Hyperautomation plays a crucial role in manufacturing by automating production lines, quality control processes, and inventory management.
Moreover Robots and AI-powered systems work collaboratively with human workers to improve production efficiency.
Healthcare:
In healthcare, Advanced Automation streamlines administrative tasks such as appointment scheduling, claims processing, and billing.
Furtherly it also aids in medical data analysis, helping physicians make more informed decisions.
Retail:
Retailers use Advanced Automation for inventory management, demand forecasting, and personalized marketing. Chatbots and virtual assistants enhance customer support and engagement.
Supply Chain:
Advanced Automation optimizes supply chain operations by tracking shipments, predicting demand, and managing inventory levels. It ensures goods reach their destinations efficiently.
Human Resources:
HR departments use Advanced Automation for candidate screening, employee onboarding, and payroll processing.
And also it frees HR professionals from manual paperwork, allowing them to focus on strategic HR initiatives.
Implementing Hyperautomation: Best Practices
Importantly Organizations looking to embrace hyperautomation should keep the following best practices in mind.
Start with a Strategy:
Develop a clear strategy that outlines your automation goals, identifies key processes for automation, and defines success metrics.
Prioritize Security:
Implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
Employee Training:
Provide comprehensive training to employees to help them adapt to the changes brought about by automation. Encourage a culture of continuous learning.
Change Management:
Effective change management is crucial. Communicate the benefits of hyperautomation to employees and involve them in the process to mitigate resistance to change.
Measure and Optimize:
Continuously monitor automated processes and gather data for analysis. Use insights to make improvements and optimize workflows further.
Scale Gradually:
Start with a few pilot projects and scale up gradually. This approach allows you to learn from initial implementations and make necessary adjustments.
Vendor Selection:
Choose technology vendors carefully. Consider factors such as scalability, reliability, and the vendor’s track record in delivering hyperautomation solutions.
Debunking Hyperautomation Myths
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding hyperautomation. Let’s debunk some of them:
Hyperautomation Replaces Humans:
One common misconception is that hyperautomation aims to replace human workers entirely.
In reality, it augments human capabilities and allows employees to focus on more valuable tasks.
Hyperautomation is Expensive:
While there are costs associated with implementing hyperautomation, the long-term benefits in terms of cost savings and efficiency outweigh the initial investment.
It’s Only for Large Enterprises:
Hyperautomation can benefit organizations of all sizes. Smaller businesses can start with automation solutions that suit their needs and budget.
One-Size-Fits-All:
There is no one-size-fits-all solution in hyperautomation. Each organization’s needs and processes are unique, and automation solutions should be tailored accordingly.
Hyperautomation is Only About Software:
While software plays a significant role, hyperautomation also involves hardware components, IoT devices, and process optimization.
The Future of Hyperautomation
The future of hyperautomation is promising and involves continuous innovation and evolution.
AI Advancements:
As AI and ML technologies advance, hyperautomation will become even more intelligent, capable of making complex decisions and adapting to changing circumstances.
Edge Computing:
Hyperautomation will leverage edge computing to process data closer to the source, reducing latency and enabling real-time automation in IoT applications.
Ethical Considerations:
In additionly With increased automation, ethical concerns around AI and data privacy will become more significant.
And also Organizations will need to address these issues transparently.
Industry-Specific Solutions:
Hyperautomation solutions will continue to become more industry-specific, addressing unique challenges and requirements in various sectors.
Collaborative Automation:
Collaborative robots (cobots) will play a more prominent role in manufacturing and other industries, as well as working alongside human workers safely and efficiently.
Conclusion
Hyperautomation represents a transformative shift in the way businesses operate, leveraging advanced technologies to streamline processes, as well as reduce costs, and enhance efficiency.
Importantly it is not a mere buzzword but a practical approach that has found applications in diverse industries.
Moreover By embracing hyperautomation and adhering to best practices, organizations can position themselves for a more productive and competitive futuer
